
Predictive maintenance is a maintenance strategy that uses data analysis tools and techniques to monitor the condition of equipment and predict when maintenance should be performed. The goal of predictive maintenance is to anticipate when equipment failure might occur and to perform maintenance activities that prevent the failure before it actually happens. This approach helps to minimize unplanned downtime and prevent costly damage to equipment, thereby increasing overall efficiency and reducing maintenance costs. Predictive maintenance often relies on techniques such as data analytics, machine learning, and sensor technology to monitor the health of equipment and identify potential issues before they lead to a breakdown.
You might be thinking by which technologies and methodologies predictive maintenance is enabled. Here are the following:
Sensor Technology: Sensors are used to monitor various parameters such as temperature, vibration, pressure, and more. These sensors collect real-time data on the operating conditions and performance of the equipment.
Data Collection and Analysis: Data collected from sensors and other sources are analyzed using various analytical tools and techniques, including machine learning algorithms. These analyses help in identifying patterns and anomalies that can indicate potential failures or degradation in the performance of the equipment.
Condition Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of the equipment’s condition allows for the detection of any deviations from the norm. This helps in predicting when maintenance is required based on the identified patterns and trends in the data.
Predictive Analytics: By using historical data and advanced algorithms, predictive maintenance can anticipate when equipment failure is likely to occur. This enables businesses to schedule maintenance activities at optimal times, reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns and minimizing downtime.
Integrated Maintenance Strategies: The insights gained from predictive maintenance can be integrated into the overall maintenance strategy of the business. This integration allows for a more efficient allocation of resources and better planning for maintenance activities, leading to improved productivity and cost savings.
Using these technologies and strategies, businesses can address potential equipment issues, reduce maintenance costs, and optimize the overall performance and reliability of their machinery and systems.
Industries that can benefit from implementing predictive maintenance strategies:
Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance is widely used in the manufacturing industry to ensure the continuous and efficient operation of production lines, machinery, and equipment.
Energy and Utilities: Power plants, utility companies, and energy production facilities can utilize predictive maintenance to monitor and manage critical infrastructure such as turbines, generators, and distribution systems.
Transportation and Logistics: Airlines, railways, shipping companies, and fleet management services can employ predictive maintenance to monitor the condition of vehicles, engines, and other transportation equipment to ensure safety and reduce downtime.
Oil and Gas: Predictive maintenance is crucial in the oil and gas industry to monitor and maintain drilling equipment, pipelines, and refineries, ensuring smooth and efficient operations while minimizing the risk of costly downtime.
Healthcare: Hospitals and healthcare facilities can use predictive maintenance to monitor and manage critical equipment such as MRI machines, X-ray equipment, and other medical devices, ensuring their reliability and minimizing disruptions to patient care.
Telecommunications: Telecommunication companies can apply predictive maintenance to manage their network infrastructure, including servers, data centers, and communication equipment, ensuring uninterrupted service for customers.
Automotive: Automotive manufacturers and service centers can utilize predictive maintenance to monitor the condition of vehicles and optimize maintenance schedules, enhancing the reliability and safety of vehicles on the road.
These industries, along with many others, can utilize predictive maintenance to improve operational efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance overall productivity and safety.

Cost of implementing Predictive Maintenance:
Understanding the costs associated with a particular initiative or project is a crucial aspect of decision-making for individuals and businesses alike. People are often interested in knowing the cost. The cost of implementing a predictive maintenance program can vary depending on several factors, including the size and complexity of the operation, the type of equipment being monitored, the scale of the predictive maintenance implementation, and the technology used. Some of the key cost components associated with implementing predictive maintenance include:
Technology Investment: This includes the cost of acquiring and installing sensors, data collection systems, and monitoring equipment. The cost can vary based on the number of sensors needed, the type of sensors required for specific equipment, and the complexity of the monitoring system.
Data Management and Analysis: Implementing a predictive maintenance program involves the cost of setting up data management infrastructure, including data storage, processing, and analysis. This may include the cost of software, data analytics tools, and skilled personnel for data analysis.
Training and Expertise: Training employees to operate and maintain the predictive maintenance system effectively is crucial. This may involve initial training costs as well as ongoing training to keep personnel updated on the latest technologies and methodologies.
Maintenance and Upkeep: Regular maintenance of the predictive maintenance system is essential to ensure its effectiveness and reliability. This includes costs associated with system updates, calibration of sensors, and regular checks to maintain the accuracy of the data collected.
Downtime and Transition Costs: During the initial implementation phase, there may be some downtime associated with installing sensors and integrating the predictive maintenance system with existing equipment. Businesses should consider the potential loss of productivity and revenue during this transition period.
Despite the initial investment, predictive maintenance can ultimately result in significant cost savings by reducing unplanned downtime, preventing costly equipment failures, and extending the lifespan of machinery and assets. The return on investment (ROI) for a predictive maintenance program can be substantial, especially in industries where equipment downtime can have a significant impact on production and revenue.
Benefits of applying Predictive Maintenance:
Predictive maintenance can provide businesses with several edges, allowing them to optimize operations, reduce downtime, and improve overall efficiency. Here are some of the significant benefits:
Cost Savings: Predictive maintenance can help companies save on maintenance costs by addressing potential issues before they lead to major breakdowns or failures. By accurately predicting maintenance needs, businesses can avoid costly unplanned downtime and emergency repairs.
Increased Equipment Uptime: By predicting when equipment is likely to fail, businesses can schedule maintenance during planned downtime, reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns. This leads to increased equipment uptime and improved overall productivity.
Extended Equipment Lifespan: Regular predictive maintenance can help businesses identify and address potential issues that could shorten the lifespan of machinery. By addressing these issues in a timely manner, companies can extend the life of their equipment and maximize their return on investment.
Improved Operational Efficiency: Predictive maintenance allows businesses to optimize their maintenance schedules, ensuring that maintenance activities are performed only when necessary. This leads to better resource allocation and improved operational efficiency.
Enhanced Safety and Reliability: By proactively identifying and addressing potential equipment failures, businesses can ensure a safer working environment for their employees. Predictive maintenance also leads to more reliable operations, reducing the risk of accidents and improving overall workplace safety.
Data-Driven Insights: Implementing predictive maintenance often involves the use of advanced sensors and data analytics, providing businesses with valuable insights into their equipment performance and maintenance needs. These insights can be used to make informed decisions and optimize maintenance strategies.
Competitive Advantage: Businesses that effectively implement predictive maintenance can gain a significant competitive advantage by reducing operational costs, improving equipment reliability, and enhancing overall productivity. This can lead to improved customer satisfaction, increased market share, and a stronger position in the industry.
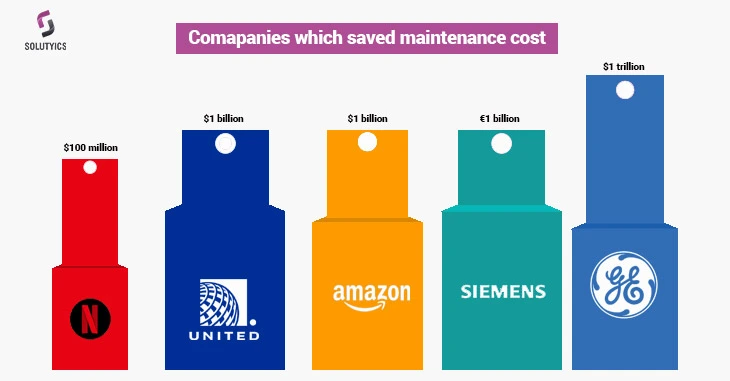
Real-world examples of firms that applied predictive:
United Airlines: United Airlines uses predictive maintenance to monitor its aircraft engines for signs of wear and tear. This allows the airline to schedule maintenance before a failure occurs, avoiding costly downtime and disruptions to its flight schedule. United Airlines estimates that predictive maintenance has saved it over $1 billion in maintenance costs since 2010.
General Electric: General Electric (GE) uses predictive maintenance to monitor its industrial equipment, such as turbines and generators. This allows GE to identify and fix potential problems before they cause costly failures. GE estimates that predictive maintenance has saved its customers over $1 trillion in downtime and repair costs.
Siemens: Siemens uses predictive maintenance to monitor its wind turbines. This allows Siemens to identify and fix potential problems before they cause turbines to fail and lose power generation. Siemens estimates that predictive maintenance has saved its customers over €1 billion in downtime and repair costs.
Netflix: Netflix uses predictive maintenance to monitor its servers. This allows Netflix to identify and fix potential problems before they cause outages and disruptions to its streaming service. Netflix estimates that predictive maintenance has saved it over $100 million in downtime costs since 2014.
Amazon: Amazon uses predictive maintenance to monitor its warehouses and delivery network. This allows Amazon to identify and fix potential problems before they cause delays and disruptions to its fulfillment process. Amazon estimates that predictive maintenance has saved it over $1 billion in costs since 2015.
These are just a few examples of how firms are using predictive maintenance to improve their operations and save money. As the technology continues to develop, predictive maintenance is expected to become even more widely used in the future.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, predictive maintenance, enabled by advanced technologies such as sensor technology, data analysis, and predictive analytics, offers businesses a proactive approach to equipment maintenance. While initial implementation costs may vary, the benefits are substantial, including cost savings, increased equipment uptime, extended equipment lifespan, improved operational efficiency, enhanced safety, and a competitive edge in the market. Real-world examples from various industries illustrate the significant impact of predictive maintenance in reducing downtime, saving costs, and improving overall operational performance. As technology continues to evolve, predictive maintenance is poised to become an indispensable strategy for businesses seeking to optimize their maintenance practices and stay ahead in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Author
Team Solutyics is a dynamic group of Analytics and AI specialists who bring together a rich mix of expertise. Their combined insights ensure that readers gain a deeper understanding of practical applications of Analytics and AI.
