
Banking analytics refers to the process of analyzing various types of data in the banking industry to gain insights and make informed decisions. It involves using advanced analytical techniques to examine customer behavior, financial trends, and risks, among other factors, with the goal of improving operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall financial performance.
Key aspects of banking analytics:
Customer segmentation: Identifying and categorizing customers based on various characteristics such as behavior, demographics, and transaction history to tailor services and marketing strategies.
Risk assessment: Evaluating and managing financial risks, including credit, market, and operational risks, to ensure the stability and security of the banking institution.
Fraud detection and prevention: Using data analysis to detect fraudulent activities and implement measures to prevent potential financial losses and maintain the trust of customers.
Predictive modeling: Utilizing statistical models and algorithms to forecast future trends, customer behavior, and potential risks, enabling proactive decision-making and strategy formulation.
Regulatory compliance: Ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements and standards by monitoring data and generating accurate reports for regulatory authorities.
Performance monitoring: Tracking and analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) such as profitability, cost management, and customer retention to assess the overall financial health and success of the bank.
Product and service optimization: Analyzing customer feedback and usage data to refine existing products and develop new services that meet the evolving needs and preferences of customers.
Market trend analysis: Studying market trends, competitor behavior, and economic indicators to make informed decisions about product offerings, interest rates, and investment strategies.
Channel optimization: Assessing the performance of different banking channels, such as online banking, mobile apps, and physical branches, to improve customer engagement and streamline banking operations.
Real-time analytics: Implementing systems that allow for the immediate analysis of data to make timely decisions, respond to customer needs quickly, and stay ahead in the dynamic banking environment.
Advantages of Banking Analytics:
Banking analytics can provide numerous advantages for financial institutions, allowing them to make more informed decisions, streamline operations, and provide better services to their customers. Some key advantages of banking analytics include:
Risk Management: Analytics can help banks assess and manage risks more effectively by identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities in their portfolios. By analyzing historical data and market trends, banks can make more accurate predictions about credit risk, market risk, and operational risk, enabling them to develop robust risk management strategies.
Improved Customer Insights: Banking analytics can help banks gain a deeper understanding of their customers’ needs, preferences, and behaviors. By analyzing customer data, banks can personalize their services, offer targeted products, and improve customer satisfaction. This can lead to increased customer retention and loyalty.
Fraud Detection and Prevention: Analytics can be used to detect and prevent fraudulent activities, such as identity theft, unauthorized transactions, and money laundering. By analyzing transaction patterns and customer behavior, banks can identify suspicious activities in real time and take immediate action to mitigate fraud risks.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Analytics can streamline banking operations by identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. By optimizing processes, banks can reduce operational costs, improve productivity, and enhance overall efficiency. This can lead to faster transaction processing, quicker customer service, and better overall performance.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Banking analytics enables data-driven decision-making by providing insights into market trends, customer behavior, and business performance. Banks can use this information to make informed decisions about product development, marketing strategies, and investment opportunities, leading to better outcomes and improved profitability.
Regulatory Compliance: Analytics can help banks ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards. By analyzing data and monitoring key risk indicators, banks can identify compliance issues and take proactive measures to adhere to regulatory guidelines, thereby avoiding penalties and maintaining a good reputation in the industry.
Personalized Marketing: Banking analytics allows institutions to create targeted marketing campaigns based on customer segmentation and behavior analysis. By delivering personalized offers and recommendations, banks can enhance their marketing effectiveness, attract new customers, and increase cross-selling opportunities.
Predictive Analytics for Financial Planning: Banks can use predictive analytics to forecast future market trends, customer demand, and economic conditions. This can help them make accurate financial projections, develop effective investment strategies, and optimize their asset and liability management, leading to improved financial planning and performance.
Overall, banking analytics plays a crucial role in enabling banks to stay competitive, mitigate risks, and deliver superior customer experiences in an increasingly complex and dynamic financial landscape.
Real World Examples of Banking Analytics:
Bank: Capital One
Use case: Customer segmentation and product development
Benefit: 15% increase in cross-selling and up-selling rates
Capital One uses analytics to segment its customers into different groups based on their demographics, transaction history, and other factors. This allows Capital One to target its marketing and product offerings more effectively. For example, Capital One might offer a different type of credit card to customers who travel frequently than to customers who don’t.
Capital One also uses analytics to develop new products and services that meet the needs of its customers. For example, Capital One used analytics to develop its Venture Rewards credit card, which is targeted at customers who travel frequently. The Venture Rewards credit card offers bonus miles on travel-related purchases and redemptions.
As a result of its use of analytics, Capital One has been able to increase its cross-selling and up-selling rates by 15%. This means that Capital One is able to sell more products and services to its existing customers.
Bank: Wells Fargo
Use case: Fraud detection
Benefit: 20% decrease in fraud losses
Wells Fargo uses analytics to detect fraudulent transactions and activities. This includes things like credit card fraud, identity theft, and money laundering. Wells Fargo has developed a number of fraud detection models that are used to identify fraudulent transactions. These models are constantly being updated and refined to keep up with the latest fraud trends.
As a result of its use of analytics, Wells Fargo has been able to decrease its fraud losses by 20%. This means that Wells Fargo is able to save money and protect its customers from fraud.
Bank: JPMorgan Chase
Use case: Risk management
Benefit: Reduced risk exposure and improved profitability
JPMorgan Chase uses analytics to improve its risk management practices. For example, the bank uses analytics to identify and mitigate credit risk, market risk, and operational risk. As a result, JPMorgan Chase has been able to reduce its risk exposure and improve its profitability.
Bank: Bank of America
Use case: Product development
Benefit: Increased customer attraction and market share
Bank of America uses analytics to develop new products and services for its customers. For example, the bank used analytics to develop its My Rewards credit card program, which offers customers personalized rewards based on their spending habits. As a result, Bank of America has been able to attract new customers and increase its market share.
Bank: HSBC
Use case: Customer service
Benefit: Improved customer satisfaction ratings
HSBC uses analytics to improve its customer service. For example, the bank uses analytics to identify customers who are likely to be dissatisfied with their service. HSBC can then target these customers with personalized outreach and support. As a result, HSBC has been able to improve its customer satisfaction ratings.
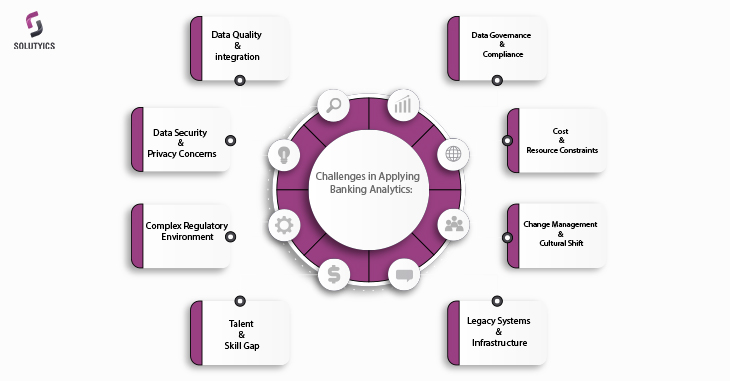
Challenges in applying banking analytics:
While banking analytics can provide significant benefits, its implementation also comes with several challenges that financial institutions must address to effectively leverage data-driven insights. Some common challenges in applying banking analytics include:
Data Quality and Integration: Ensuring the quality, consistency, and integration of data from various sources can be a significant challenge. Poor data quality and siloed data can lead to inaccurate analysis and flawed insights, impacting decision-making and the overall effectiveness of analytics initiatives.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns: Managing sensitive customer data while ensuring security and compliance with regulatory requirements is a critical challenge. Banks must implement robust data security measures to safeguard customer information and maintain privacy, especially in the face of evolving cybersecurity threats and stringent data protection regulations.
Complex Regulatory Environment: Adhering to a complex and ever-evolving regulatory landscape poses a significant challenge for banks. Implementing analytics solutions while complying with various regulatory requirements, such as data protection laws and financial reporting standards, requires significant resources and expertise.
Talent and Skill Gap: Banks often face challenges in hiring and retaining skilled professionals with expertise in data analysis, data science, and banking domain knowledge. Building a team with the necessary analytical skills and financial expertise can be a time-consuming and costly process.
Legacy Systems and Infrastructure: Many banks struggle with legacy systems and outdated infrastructure that may not be compatible with modern analytics tools and technologies. Integrating new analytics solutions with existing systems can be complex and costly, requiring significant investments in technology upgrades and system modernization.
Change Management and Cultural Shift: Implementing a data-driven culture within a traditional banking environment can be challenging. Encouraging employees to embrace analytics-driven decision-making and fostering a culture of innovation and continuous learning may require changes in organizational structure, processes, and employee mindset.
Cost and Resource Constraints: Implementing robust analytics capabilities often requires substantial investments in technology, infrastructure, and human resources. Limited budgets and resource constraints can hinder the adoption of advanced analytics solutions, especially for smaller or mid-sized banks.
Data Governance and Compliance: Establishing effective data governance practices and ensuring compliance with data management regulations can be complex. Banks must develop comprehensive data governance frameworks to manage data effectively, maintain data integrity, and meet regulatory requirements.
Overcoming these challenges requires a strategic approach that involves a combination of technology investments, talent development, regulatory compliance measures, and organizational changes to foster a data-driven culture and maximize the benefits of banking analytics.
Conclusion:
In summary, banking analytics is a powerful tool that helps banks understand their customers, manage risks, and improve operations. Real-world examples from leading banks like Capital One and Wells Fargo demonstrate its effectiveness in boosting customer satisfaction and reducing fraud. However, challenges such as data quality, security, and talent acquisition must be addressed. Despite these hurdles, banking analytics remains crucial for banks to stay competitive and customer-focused in today’s fast-paced financial environment.
Author
Team Solutyics is a dynamic group of Analytics and AI specialists who bring together a rich mix of expertise. Their combined insights ensure that readers gain a deeper understanding of practical applications of Analytics and AI.
