
Skill gap analysis is a process that organizations use to identify the difference between the skills that employees currently possess and the skills they need to meet organizational objectives. This analysis helps organizations understand the skills required for success and can inform training and development initiatives.
In a previous post, we delved into the fascinating world of HR Predictive Analytics, exploring how data-driven insights can revolutionize human resource management. Today, we shift our focus to a crucial aspect of talent development—conducting skill gap analysis. Here are the steps typically used in a skill gap analysis:
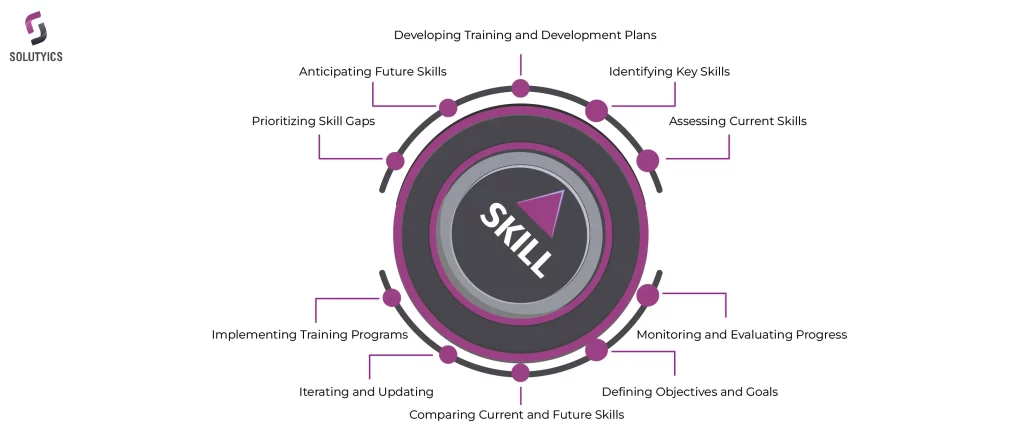
1.Define Objectives and Goals:
Clearly define the overall objectives and goals of your organization or a specific department. These could include business objectives, growth targets, or specific project goals.
2.Identify Key Skills:
Determine the critical skills and competencies required to achieve the defined objectives. These could include technical skills, soft skills, leadership abilities, or industry-specific knowledge.
3.Assess Current Skills:
Evaluate the existing skills of your workforce. This can be done through surveys, performance appraisals, interviews, or other assessment methods. Identify the skills that employees currently possess.
4.Identify Future Skills:
Anticipate the skills that will be needed in the future. Consider industry trends, technological advancements, and changes in the business environment. These skills should align with your organization’s strategic goals.
5.Compare Current and Future Skills:
Analyze the gap between the current skills and the future skills required. This comparison will highlight areas where there is a deficiency in skills and where development efforts are needed.
6.Prioritize Skill Gaps:
Prioritize the identified skill gaps based on their impact on organizational objectives and goals. Some skills may be more critical than others, and addressing high-priority gaps should be a priority.
7.Develop Training and Development Plans:
Based on the prioritized skill gaps, create training and development plans. This could involve implementing training programs, workshops, mentoring, or other learning initiatives to bridge the gaps.
8.Implement Training Programs:
Roll out the training programs and initiatives designed to address the skill gaps. Ensure that employees have access to the necessary resources and support for their development.
9.Monitor and Evaluate Progress:
Regularly monitor and evaluate the progress of employees in acquiring the required skills. Assess the effectiveness of the training programs and make adjustments as needed.
10.Iterate and Update:
The skill gap analysis process should be iterative. As the business environment evolves, reassess the skills needed and repeat the analysis to ensure that the organization’s workforce remains equipped to meet its objectives.
By following these steps, organizations can systematically identify, address, and close the skill gaps within their workforce, ultimately enhancing their ability to achieve strategic goals.
Types of Skills Gap Analysis
Skills gap analysis can be conducted in various ways, depending on the specific goals, scope, and context of the analysis. Here are several types of skills gap analysis:
1.Individual Skills Gap Analysis:
Focus: Assessing the gap in skills for an individual employee.
Purpose: Personalized development plans to enhance specific competencies required for the current role or future career growth.
2.Team-Based Skills Gap Analysis:
Focus: Evaluating the collective skills of a team or department.
Purpose: Identifying team strengths and weaknesses, fostering collaboration, and addressing gaps that may impact team performance.
3.Departmental Skills Gap Analysis:
Focus: Analyzing skills within an entire department or functional area.
Purpose: Aligning the skills of a department with its strategic objectives and ensuring that the workforce can collectively meet organizational goals.
4.Organizational Skills Gap Analysis:
Focus: Assessing skills across the entire organization.
Purpose: Identifying overarching skill gaps that may affect the organization’s ability to achieve its mission and strategic objectives.
5.Technical Skills Gap Analysis:
Focus: Evaluating proficiency in technical skills (e.g., programming languages, software tools).
Purpose: Ensuring that employees possess the technical expertise required to perform their job functions effectively.
6.Soft Skills Gap Analysis:
Focus: Assessing interpersonal and behavioral skills (e.g., communication, teamwork).
Purpose: Enhancing employees’ soft skills to improve collaboration, communication, and overall workplace effectiveness.
7.Leadership Skills Gap Analysis:
Focus: Evaluating leadership and managerial competencies.
Purpose: Identifying gaps in leadership skills to cultivate a strong leadership pipeline and support succession planning.
8.Future Skills Gap Analysis:
Focus: Anticipating skills needed for future roles or industry trends.
Purpose: Preparing the workforce for upcoming changes in technology, industry standards, or job requirements.
9.Cross-Functional Skills Gap Analysis:
Focus: Assessing skills that cut across different functional areas.
Purpose: Ensuring that employees possess interdisciplinary skills necessary for collaboration and problem-solving in a cross-functional environment.
10.Succession Planning Skills Gap Analysis:
Focus: Evaluating skills necessary for future leadership roles.
Purpose: Identifying and developing employees with the potential to fill key leadership positions within the organization.
11.Industry-Specific Skills Gap Analysis:
Focus: Assessing skills required within a specific industry.
Purpose: Ensuring that the workforce is equipped with the skills needed to navigate industry-specific challenges and advancements.
12.Global Skills Gap Analysis:
Focus: Evaluating skills on a global scale, considering diverse cultural and regional needs.
Purpose: Identifying skill gaps that may vary across different regions or markets where the organization operates.
The choice of the skills gap analysis type depends on the organizational objectives, the level of granularity needed, and the specific challenges or opportunities the organization is addressing. Combining multiple types of skills gap analyses may provide a more comprehensive understanding of the overall skill landscape within an organization.
Tools and Software Solutions for Effective Skills Gap Analysis:
Several tools and software applications can facilitate the process of skills gap analysis. These tools are designed to help organizations assess the skills of their workforce, identify gaps, and plan for training and development. Here are some commonly used tools and software for skills gap analysis:
1.Learning Management Systems (LMS):
Examples: Moodle, Blackboard, Canvas
Features: LMS platforms can track employee training, manage courses, and generate reports on the skills acquired by employees. They are useful for monitoring progress and identifying gaps in knowledge.
2.Skill Assessment Platforms:
Examples: ProProfs, Mettl, Skillsoft
Features: These platforms offer pre-built assessments or customizable tests to evaluate the current skills of employees. They often provide detailed reports on individual and overall performance.
3.Employee Performance Management Software:
Examples: BambooHR, Workday, SuccessFactors
Features: Performance management tools can include features for goal setting, performance reviews, and skill tracking. They help in identifying gaps between expected and actual performance.
4.Survey and Feedback Tools:
Examples: SurveyMonkey, Typeform, Qualtrics
Features: Surveys and feedback tools can be used to gather insights from employees about their perceived skills, areas of improvement, and training needs.
5.Competency Management Systems:
Examples: Talentsoft, Cornerstone OnDemand, Saba
Features: These systems focus on managing and assessing employee competencies. They often include features for skills mapping, competency assessments, and development planning.
6.Data Analytics and Business Intelligence Tools:
Examples: Tableau, Power BI, Google Data Studio
Features: Analytics tools can help analyze workforce data, identify trends, and visualize skill-related insights. They are valuable for making data-driven decisions in talent development.
7.HRIS (Human Resources Information System):
Examples: Workday, SAP SuccessFactors, ADP
Features: HRIS solutions often include modules for talent management, training, and development. They can help in tracking employee skills, competencies, and training histories.
8.Customized Spreadsheets and Databases:
Examples: Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, Airtable
Features: Organizations may use customized spreadsheets or databases to collect and analyze data related to employee skills. This can be a cost-effective solution for smaller businesses.
9.Project Management Tools:
Examples: Asana, Trello, Jira
Features: In some cases, project management tools can be used to track skills required for specific projects. This can help identify gaps in project teams and inform training needs.
10.Online Training Platforms:
Examples: Udemy for Business, LinkedIn Learning, Coursera for Business
Features: These platforms offer a wide range of courses that employees can take to develop specific skills. They often provide analytics to track progress and completion rates.
When selecting tools for skills gap analysis, it’s essential to consider the specific needs and goals of the organization. Integration with existing systems and scalability should also be taken into account to ensure a seamless and effective skills development process.
Implementing an Effective Skills Gap Analysis
In order to bridge the divide between current employee skills and the skills required to meet organizational objectives, a well-executed skills gap analysis is essential. Follow these steps to implement an effective skills gap analysis:
1. Engage Stakeholders:
Objective: Ensure alignment with organizational goals.
Action: Collaborate with key stakeholders, including department heads, HR, and team leaders, to define specific objectives and performance expectations.
2. Define Target Roles and Competencies:
Objective: Identify the skills needed for success.
Action: Clearly outline the competencies and skills required for each role. Consider both technical skills and soft skills relevant to organizational objectives.
3. Select Assessment Methods:
Objective: Gather accurate data on current skills.
Action: Choose appropriate assessment methods such as surveys, performance appraisals, or skills tests. Use a mix of quantitative and qualitative data for a comprehensive view.
4. Utilize Skill Assessment Tools:
Objective: Streamline the evaluation process.
Action: Implement skill assessment tools or platforms to efficiently collect and analyze data. These tools can automate assessments and provide detailed reports.
5. Collect Employee Input:
Objective: Capture employee perspectives.
Action: Conduct surveys or interviews to gather insights directly from employees. Ask about their perceived strengths, weaknesses, and areas for skill enhancement.
6. Prioritize Skill Gaps:
Objective: Focus on high-impact areas.
Action: Analyze assessment results and prioritize skill gaps based on their impact on organizational objectives. Identify critical skills that need immediate attention.
7. Develop Training Plans:
Objective: Create targeted development initiatives.
Action: Based on prioritized gaps, design training and development plans. Incorporate a mix of formal training programs, workshops, and on-the-job learning experiences.
8. Explore External Resources:
Objective: Leverage external expertise.
Action: Consider partnerships with external training providers, online learning platforms, or industry experts to supplement internal training efforts.
9. Implement Training Programs:
Objective: Enable skill development.
Action: Roll out the training programs, ensuring accessibility and support for employees. Track participation and monitor progress to ensure engagement.
10. Regularly Review and Update:
Objective: Adapt to changing needs.
Action: Conduct regular reviews of skills and competencies. Update the skills gap analysis as the business landscape evolves, ensuring continuous alignment with organizational goals.
11. Encourage Continuous Learning Culture:
Objective: Foster a culture of ongoing development.
Action: Promote a mindset of continuous learning within the organization. Encourage employees to take ownership of their development and seek opportunities for growth.
Performing a skill gap analysis involves a focused process to identify the disparity between existing skills and those needed to achieve specific objectives. Begin by defining the goals and pinpointing the relevant skills required for success. Choose the target group—whether individuals, teams, or entire departments—and select appropriate assessment methods such as surveys or skills tests. Administer assessments and analyze the results to identify priority skill gaps.
Develop targeted action plans, incorporating both formal training programs and on-the-job learning. Implement these initiatives, regularly evaluating and adjusting based on participant feedback. Make skill gap analysis an ongoing, iterative process to ensure continuous improvement and alignment with evolving organizational needs and goals.
How analytics can be utilized at different stages of the skills gap analysis process:
Analytics plays a crucial role in skills gap analysis by providing organizations with the ability to gather, interpret, and act upon data related to the current and future skills of their workforce. Here’s a breakdown of how it can be utilized at different stages of the skills gap analysis process:
1. Objective Setting:
Use Historical Data: Analyze past performance data to identify trends in employee skills and areas where improvement is needed.
Benchmarking: Utilize industry benchmarks to set realistic goals and objectives for skill development.
2. Skills Identification:
Data-driven Insights: Leverage data analytics tools to identify skills that are currently in demand in the industry.
Trend Analysis: Analyze industry reports and trends to understand emerging skills that may be crucial for future success.
3. Current Skills Assessment:
Performance Metrics: Use analytics to gather data from performance metrics, such as productivity, efficiency, and project outcomes.
Learning Platforms Analysis: Evaluate data from learning management systems to understand the effectiveness of current training initiatives.
4. Future Skills Anticipation:
Predictive Analytics: Utilize predictive analytics to forecast future skill requirements based on current trends and industry projections.
Technological Forecasting: Analyze technological advancements and industry changes to anticipate skills needed in the future.
5. Skills Gap Quantification:
Data Visualization: Use analytics tools to create visualizations that represent the gap between current and required skills.
Quantitative Analysis: Employ analytics to quantify the extent of the skills gap, providing numerical insights.
6. Data-driven Prioritization:
Impact Assessment: Use analytics to assess the potential impact of each skill gap on organizational objectives.
Priority Ranking: Apply data-driven models to prioritize skill gaps based on their importance and urgency.
7. Training Plan Development:
Learning Effectiveness Analysis: Analyze historical learning and development data to understand the effectiveness of past programs.
Predictive Models: Use predictive analytics to determine the most effective methods for addressing specific skill gaps.
8. Real-time Monitoring:
Engagement Tracking: Utilize analytics to track employee engagement with training programs in real-time.
Dashboard Implementation: Implement dashboards providing real-time updates on skill development metrics.
9. Progress Evaluation:
Analytics for Progress Tracking: Use analytics to monitor the progress of individuals and teams in acquiring new skills.
Performance Analytics: Implement data-driven performance evaluations to measure the impact of training on actual job performance.
10. Continuous Iteration and Updating:
Trend Analysis: Employ analytics to continuously analyze industry trends and update skill requirements accordingly.
Feedback Analytics: Utilize feedback analytics to assess the effectiveness of the skills gap analysis process and make iterative improvements.
By incorporating analytics throughout these stages, organizations can make informed decisions, allocate resources efficiently, and ensure that their workforce is equipped with the skills necessary to meet current and future challenges. It transforms the skills gap analysis from a subjective assessment to an evidence-based, data-driven strategy for talent development.
For those interested in the transformative power of artificial intelligence, our series on the future of AI has delved into its impact across diverse sectors. Check out our insights on AI in Medicine, Construction Analytics, and Public Sector Analytics.

Conclusion:
In summary, a well-executed skill gap analysis is vital for organizations striving to align workforce skills with strategic objectives. By systematically assessing current skills, anticipating future needs, and prioritizing gaps, organizations can develop targeted training plans. Regular reviews and a commitment to continuous learning ensure adaptability and sustained success in a dynamic business environment. The process is not a one-time event but an ongoing, iterative strategy for optimizing workforce capabilities.
FAQs
Q1: What is a skill gap analysis, and why is it important for organizations?
A1: A skill gap analysis is a process used by organizations to identify the disparity between the current skills of their workforce and the skills required to meet organizational objectives. It is crucial for understanding the skills necessary for success, informing targeted training initiatives, and ensuring alignment with strategic goals.
Q2: How can organizations prioritize skill gaps identified in the analysis?
A2: To prioritize skill gaps, organizations should assess their impact on overall objectives and goals. Some skills may be more critical than others, and prioritizing ensures that high-impact areas are addressed first. This allows for the efficient allocation of resources and a focused approach to skill development.
Q3: What types of skills gap analyses can organizations perform, and how do they differ?
A3: Organizations can conduct various types of skills gap analyses, including individual, team-based, departmental, organizational, technical, soft skills, leadership, future skills, cross-functional, succession planning, industry-specific, and global analyses. Each type focuses on different aspects, allowing organizations to tailor their approach based on specific goals, scope, and contextual needs.
Author
Team Solutyics is a dynamic group of Analytics and AI specialists who bring together a rich mix of expertise. Their combined insights ensure that readers gain a deeper understanding of practical applications of Analytics and AI.

Comment (1)
I enjoy your website, obviously, but you should check the spelling on a number of your posts. A number of them have numerous spelling errors, which makes it difficult for me to tell the truth, but I will definitely return.