
In the dynamic landscape of modern business, finding innovative ways to increase revenue and enhance customer experiences has become paramount. Two such strategies that have gained immense traction are cross-selling and upselling. Utilizing data analytics in these strategies has proven to be revolutionary, enabling businesses to identify opportunities, tailor offers, and boost their bottom line. If you’re a beginner looking to delve into the world of cross-selling and upselling, this guide is here to provide you with a comprehensive understanding.
What is Cross-Selling?
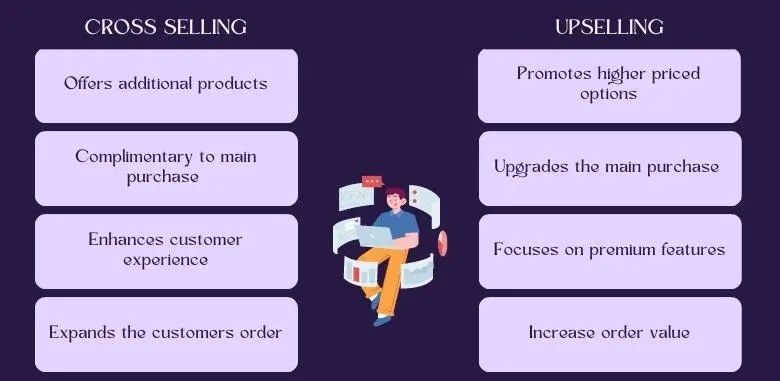
Cross-selling is a sales and marketing strategy in which a company encourages customers to purchase additional products or services that complement or relate to the primary product or service they are already interested in or have already purchased. The goal of cross-selling is to increase the overall value of each customer transaction and enhance the customer’s experience by suggesting items that could enhance their use or enjoyment of the original product.
Cross-selling is a win-win strategy for both customers and businesses. Customers benefit by discovering complementary products that could enhance their primary purchase, and businesses benefit by increasing their revenue per transaction and building stronger customer relationships.
Effective cross-selling requires a good understanding of the customer’s needs and preferences, as well as careful consideration of which additional products or services make sense to offer. It’s important to ensure that the cross-sell recommendations are relevant, valuable, and not overly pushy, as customers may become frustrated or disinterested if they feel pressured into buying something they don’t need.

What is Upselling?
Upselling is a sales technique where a business or salesperson encourages a customer to purchase a more expensive or upgraded version of a product or service or to add extra features or enhancements to their original purchase. The goal of upselling is to increase the value of the sale by convincing the customer to opt for higher-priced options or additional offerings.
Unlike cross-selling, which involves suggesting related products or services, upselling focuses on convincing the customer to spend more on the same product or service they are already interested in. This can be done by highlighting the benefits and advantages of the higher-priced options, emphasizing the added value they bring, and demonstrating how they meet the customer’s needs more effectively.
Effective upselling requires a good understanding of the customer’s preferences and needs, as well as the ability to communicate the value of the higher-priced options without being overly pushy. The goal is to help the customer make an informed decision that aligns with their needs and budget, rather than pressuring them into a purchase they may not truly want.
When done right, upselling can lead to increased revenue for the business, higher average transaction values, and improved customer satisfaction if the customer genuinely benefits from the upsold product or service. However, it’s important to strike a balance and ensure that the upsell recommendations are relevant, transparent, and respectful of the customer’s choices.
Difference between Upselling and Cross-Selling:
While both upselling and cross-selling aim to increase the value of a customer’s purchase, they target different aspects. Upselling focuses on enhancing the current purchase by encouraging customers to opt for a more premium option. Cross-selling, on the other hand, aims to offer complementary products that enhance the main purchase.
How analytics is used in cross-selling and upselling?
Analytics plays a crucial role in both cross-selling and upselling strategies, helping businesses identify opportunities, make informed decisions, and personalize their offers to maximize effectiveness. Here’s how analytics is used in cross-selling and upselling:
Cross-Selling Analytics:
- Data Analysis: Analytics starts with collecting and analyzing customer data, including purchase history, browsing behavior, and demographic information. By examining this data, businesses can identify patterns and relationships between products that are frequently purchased together.
- Market Basket Analysis: This technique examines the combinations of products that tend to be bought together. It helps identify potential cross-selling opportunities by revealing which products have a strong association.
- Segmentation: Analytics can segment customers based on their preferences, behaviors, and demographics. These segments help tailor cross-selling offers to specific groups, making the offers more relevant and appealing.
- Recommendation Systems: Advanced analytics and machine learning can power recommendation algorithms that suggest relevant cross-selling products to customers. These algorithms learn from customer interactions and historical data to provide personalized suggestions.
- Predictive Modeling: Analytics can build predictive models that estimate the likelihood of a customer purchasing a particular cross-sell product. This helps businesses target the right customers with the right offers.
- A/B Testing: Analytics is used to run A/B tests, comparing different cross-selling strategies to determine which ones yield the best results. This allows for data-driven optimization of cross-selling approaches.
Upselling Analytics:
- Customer Segmentation: Similar to cross-selling, segmentation is crucial for upselling. Analytics helps categorize customers based on their spending behavior, preferences, and past purchases, enabling businesses to tailor upselling offers accordingly.
- Product Comparison Analysis: Analytics helps identify key features and benefits of higher-priced products or packages. This information is used to demonstrate the added value to the customer.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) Analysis: Analytics calculates the potential value a customer could bring over their entire relationship with the business. This informs the decision to invest in upselling efforts for specific customers.
- Price Sensitivity Analysis: By analyzing customer responses to different pricing strategies, businesses can determine the optimal pricing points for upsell offers.
- Personalization: Analytics enables personalized upsell offers based on individual customer preferences, buying history, and behavior. This personal touch increases the likelihood of a successful upsell.
- Conversion Rate Analysis: Analytics tracks the success rates of different upselling strategies, helping businesses identify which approaches are most effective and make data-backed adjustments.
In both cross-selling and upselling, analytics provides insights that guide decision-making, improve targeting, enhance customer experiences, and increase the likelihood of successfully increasing the value of each customer transaction.
Let’s try to understand cross-sell and upsell with an example:
Scenario: Online Electronics Store
A customer visits an online electronics store with the intention of buying a new laptop.
Cross-Sell Example:
The customer selects a laptop to add to their cart. As they proceed to checkout, the online store’s system suggests complementary products that other customers frequently buy with laptops, such as laptop bags, external hard drives, and laptop cooling pads. This is a cross-selling strategy because the store is recommending related products that enhance the customer’s laptop purchase.
Upsell Example:
The customer selects a mid-range laptop with standard specifications. As they view the laptop’s details, a pop-up notification appears, offering an upgraded version of the same laptop with a faster processor, more RAM, and a larger SSD. The notification explains how the upgraded version will provide better performance for multitasking and running resource-intensive applications. This is an upselling strategy because the store is encouraging the customer to choose a higher-priced version of the same product with enhanced features.
In the cross-sell example, the store is suggesting additional products that complement the customer’s primary purchase. This encourages the customer to expand their shopping basket beyond the laptop itself.
In the upsell example, the store is encouraging the customer to consider a more advanced version of the same product they initially chose. The emphasis is on convincing the customer to spend more by highlighting the benefits of the upgraded specifications.
Read more about How can Businesses use ChatGpt by tapping the potential of AI.
How Do You Measure Cross-Sell and Upsell?
Measuring the effectiveness of cross-selling and upselling efforts involves analyzing relevant metrics to determine how successful these strategies are in increasing revenue and enhancing customer transactions. Here are some key metrics and steps for measuring cross-sell and upsell performance:
Conversion Rates:
- Cross-Sell Conversion Rate: This measures the percentage of customers who accepted a cross-selling offer out of the total number of customers who were presented with the offer. It’s calculated as (Number of Cross-Sell Conversions / Total Number of Customers Offered Cross-Sell) * 100.
- Upsell Conversion Rate: This calculates the percentage of customers who accepted an upselling offer out of the total number of customers who were presented with the offer. It’s calculated as (Number of Upsell Conversions / Total Number of Customers Offered Upsell) * 100.
Average Transaction Value:
- Cross-Sell Average Transaction Value: This measures the average value of a transaction when cross-selling is successful. It’s calculated as Total Revenue from Cross-Sell / Number of Cross-Sell Conversions.
- Upsell Average Transaction Value: This calculates the average value of a transaction when upselling is successful. It’s calculated as Total Revenue from Upsell / Number of Upsell Conversions.
- Higher Average Transaction Value: indicates customers are spending more per transaction, potentially increasing overall revenue. Lower Average Transaction Value suggests that customers are sticking to basic options without many additional purchases.
Revenue Impact:
- Calculate the total revenue: generated from successful cross-selling and upselling efforts over a specific time period. Compare this to the revenue generated without these strategies to determine the revenue impact.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV):
- Measure how cross-selling and upselling: impact the CLV of customers. Determine if customers who engage in these strategies have higher CLV compared to those who don’t.
Product Affinity Analysis:
- Analyze which products: are commonly purchased together in cross-selling efforts. This can help identify strong product associations and guide future cross-selling strategies. (Product Association: A pattern where customers tend to buy specific products together, indicating a connection or preference for using those items in combination.)
Churn Rate:
- Monitor whether cross-selling and upselling: efforts lead to lower churn rates (customer attrition). If customers are finding value in the additional offerings, they may be more likely to stay loyal.
Customer Satisfaction and Feedback:
- Gather feedback: from customers who have experienced cross-selling and upselling. Positive feedback can indicate that the strategies are enhancing the customer experience.
A/B Testing:
- A/B testing: involves comparing two versions of a webpage, email, or other content to determine which version performs better, helping to optimize cross-selling and upselling strategies.
- Conduct A/B tests to compare the performance of different cross-selling and upselling strategies. Measure which strategies yield the best results in terms of conversion rates, revenue, and customer satisfaction.
Return on Investment (ROI):
- Calculate the ROI: of cross-selling and upselling efforts by comparing the costs associated with implementing these strategies (e.g., marketing costs, staff training) to the additional revenue generated. ROI = ((Additional Revenue – Cost of Implementation) / Cost of Implementation) × 100
By tracking these metrics and analyzing the data, businesses can assess the effectiveness of their cross-selling and upselling strategies. Regular monitoring and adjustments based on the insights gained will help optimize these techniques and improve their impact on the company’s bottom line.

Ways to Successfully Use Cross-Sell and Upsell
Successfully using cross-selling and upselling techniques requires a strategic and customer-centric approach. Here are some effective ways to implement cross-sell and upsell strategies:
Understand Customer Needs:
- Prioritize understanding your customers’ needs and preferences. This knowledge forms the foundation for offering relevant additional products or upgrades.
Segmentation:
- Segment your customer base into groups with similar characteristics or buying behaviors. This allows you to tailor cross-selling and upselling offers to each segment’s preferences.
Personalization:
- Use customer data to personalize recommendations. Customers are more likely to respond positively to offers that align with their past behaviors and interests.
Contextual Placement:
- Place cross-selling and upselling offers in contexts where they make sense. For instance, when a customer adds an item to their cart or during the checkout process.
Relevant Offers:
- Ensure that the additional products or upgrades you’re suggesting are genuinely relevant and provide value to the customer’s original purchase.
Transparency:
- Clearly communicate the benefits of the additional product or upgrade. Explain how it enhances the customer’s experience or solves a problem.
Highlight Value:
- Emphasize the value the customer will receive from the additional product or upgrade. Explain how it addresses their specific needs or desires.
Social Proof:
- Use social proof by showcasing customer reviews or testimonials that highlight the benefits of the additional product or upgrade.
Educational Content:
- Provide educational content that explains how the additional product or upgrade can enhance the customer’s experience. This can be in the form of blog posts, videos, or guides.
Test and Iterate:
- Continuously test different cross-selling and upselling strategies to determine what resonates best with your audience. Analyze the results and make adjustments accordingly.
Train Sales and Support Teams:
- Train your sales and customer support teams to effectively communicate and present cross-selling and upselling offers to customers.
Post-Purchase Engagement:
- After a customer makes a purchase, engage them with follow-up communications that suggest complementary products or upgrades.
Monitor Results:
- Regularly monitor key metrics such as conversion rates, average transaction value, and revenue generated from cross-selling and upselling efforts. Use these insights to refine your strategies.
Ethics and Customer Value:
- Always prioritize the customer’s best interests. Focus on offering products or upgrades that genuinely enhance their experience and provide value.
Feedback Loop:
- Encourage customer feedback on the additional products or upgrades they’ve purchased. This information can guide future improvements and strategies.
By combining these approaches, businesses can create cross-selling and upselling strategies that not only increase revenue but also contribute positively to customer experience and satisfaction.
Cross-Selling Use Case with Solutyics
Goal: Enhance the average transaction value for our client by implementing a cross-selling strategy through Solutyics expertise.
Actions: Solutyics collaborated with its client to develop a data-driven cross-selling strategy. Using advanced analytics and AI, Solutyics analyzed XYZ’s customer data to identify patterns and product affinities. They segmented the customer base based on preferences and purchasing behavior.
Next, Solutyics implemented a recommendation system that showcased complementary products to customers during their online shopping experience. Additionally, they designed personalized email campaigns suggesting related products based on customers’ previous purchases.
Results:
- Increased Average Transaction Value: The cross-selling strategy led to an increase in the average transaction value. Customers were more likely to add suggested complementary products to their purchases, resulting in higher sales revenue per transaction.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Customers appreciated the personalized product recommendations, which demonstrated an understanding of their preferences. This led to enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Enhanced Revenue: The implementation of the cross-selling strategy contributed to a noticeable boost in overall revenue for XYZ Corporation.
By leveraging Solutyics data-driven approach and expertise in AI and analytics, our client implemented a cross-selling strategy that not only increased revenue but also provided a better shopping experience for their customers. This case exemplifies how Solutyics transforms data into valuable insights and actionable strategies to drive business growth and customer satisfaction.
Author
Team Solutyics is a dynamic group of Analytics and AI specialists who bring together a rich mix of expertise. Their combined insights ensure that readers gain a deeper understanding of practical applications of Analytics and AI.
